EVA vs. TPE: Which Material is Best for Your Next Project?
Choosing the right material can make or break your product’s performance, durability, and market appeal. In the world of polymers, EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) and TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) are two of the most popular contenders. But which one truly aligns with your specific needs?
Quick Summary: The Core Difference
The primary difference lies in their chemical versatility and sustainability. While EVA is a foam-based polymer championing superior shock absorption and cost-effectiveness, TPE is a sophisticated blend of rubber and plastic that offers higher durability, better UV resistance, and full recyclability. If you need maximum cushioning, choose EVA; if you prioritize longevity and eco-friendliness, TPE is the superior choice.
Understanding the Materials: A Deep Dive
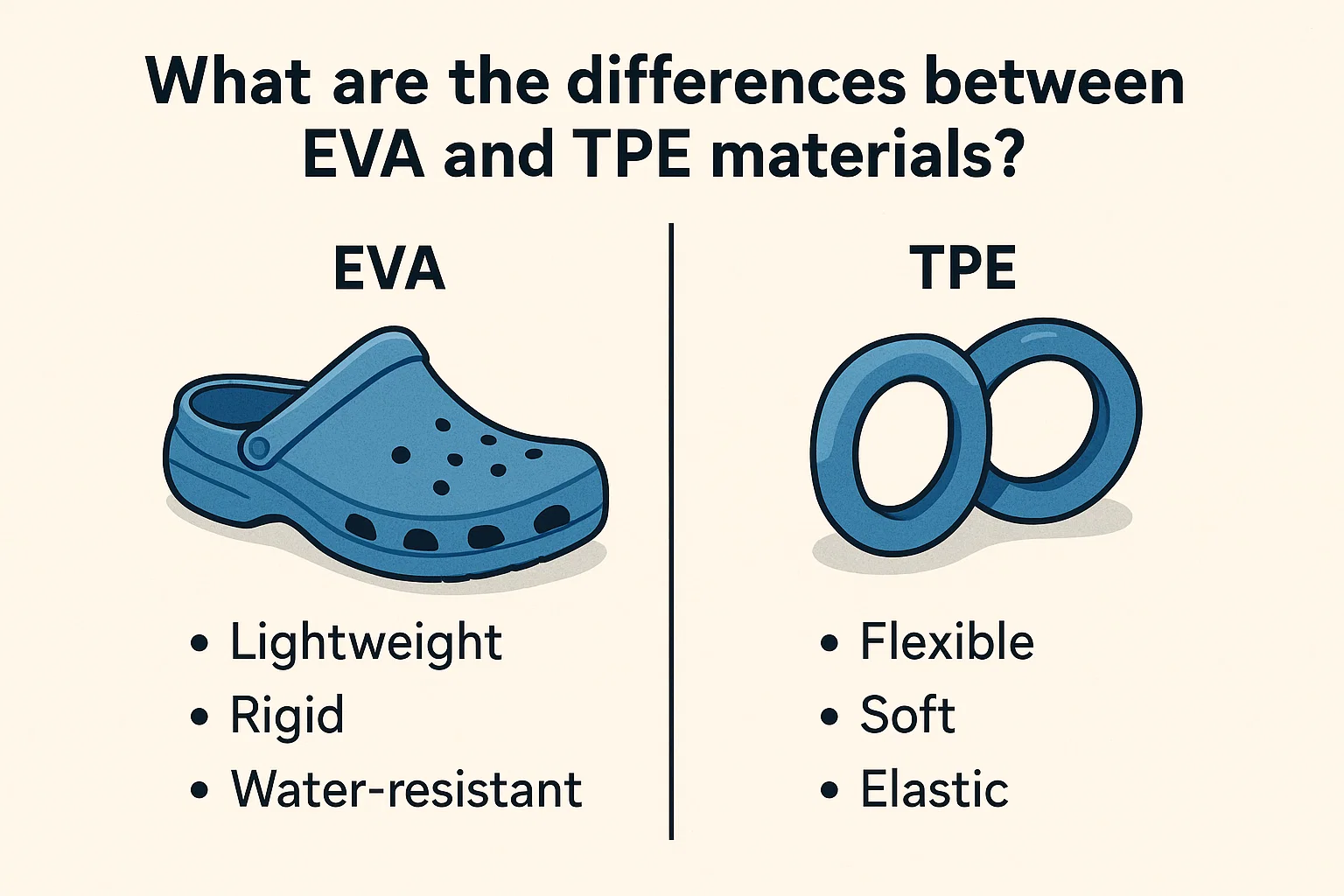
What is EVA?
EVA is an elastomeric polymer that produces materials which are “rubber-like” in softness and flexibility. It is the industry standard for lightweight cushioning.
Best for: Footwear midsoles, protective sports gear, and budget-friendly yoga mats.
What is TPE?
TPE is a high-performance material that combines the easy processing of plastics with the elasticity of rubber. It is often referred to as “green rubber.”
Best for: High-end eco-friendly yoga mats, medical tubing, and automotive seals.
Key Comparison Factors
1. Durability & Resilience
When it comes to “memory” and long-term use, TPE takes the lead. TPE products maintain their shape even after repeated stretching or compression. Furthermore, TPE offers exceptional resistance to UV rays and chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor environments where EVA might degrade or harden over time.
2. Environmental Impact (E-E-A-T Focus)
As sustainability becomes a decisive factor for modern buyers, understanding the life cycle of your material is crucial.
- TPE: 100% Recyclable. It can be melted down and reused, significantly reducing the carbon footprint.
- EVA: Harder to recycle. Most EVA foam products end up in landfills at the end of their life cycle.
3. Performance & Texture
TPE generally provides a superior grip (non-slip surface) even when wet, which is why professional-grade yoga mats prefer TPE. EVA, while extremely soft, can become slippery when exposed to sweat or moisture, although its shock absorption per millimeter is often higher than TPE.
Pros and Cons: Direct Comparison
Advantages of TPE
- Eco-friendly & Recyclable
- Excellent UV & Weather resistance
- Superior non-slip grip
- Greater elasticity & recovery
Limitations of TPE
- Higher raw material cost
- Can be heavier than low-density EVA
Advantages of EVA
- Ultra-lightweight
- Exceptional shock absorption
- Highly cost-effective
- Water-resistant (closed-cell)
Limitations of EVA
- Difficult to recycle
- Lower resistance to heat/UV
- Can “flatten” over time
Technical Specification Table
| Feature | EVA Material | TPE Material |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Soft & Cushioning | Highly Elastic & Stretchable |
| Longevity | Moderate | High (Resistant to aging) |
| Recyclability | Low | High (Eco-friendly) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Typical Cost | Budget-Friendly | Premium / Mid-range |
Strategic Decision Guide: Which should you choose?
Choose EVA if: You are designing products where lightweight comfort and cost-efficiency are the top priorities, such as disposable packaging, casual footwear, or children’s toys.
Choose TPE if: You are targeting the premium market, where sustainability, skin-friendly properties, and long-term durability under harsh conditions are non-negotiable.
Not sure which grade is right for your application? Our engineering team can provide a custom material analysis to optimize your product performance.
Get a Professional Material ConsultationExpertise Note: This comparison is based on standard industrial grades. Specific properties can be modified during the compounding process to meet bespoke requirements.